If you do a search on "what is semantic html", you'll end up with quite a few links – most giving examples like <div> <span> <button> <nav> and many more.
Dig a bit deeper though. And ask more questions. In particular, search on HTML attributes. If you include those in tags, is it still semantic?
The answer is really simple. Of course it is. Here are a few examples.
Can an img tag stand on its own? No, it requires at least one attribute: src. You have to give the "img" context, an image to load and a source (src). Can a hyperlink tag stand on its own? No, it requires at least one attribute: href. You have to give the "a" context, a target location for the link to apply.
There are no restrictions on attributes, they form a part of a tag and are considered semantic in their very nature.
I have chosen to focus on two attributes for my "classless" CSS framework. The one that I prefer, if it can be labelled as such, is the "role" attribute. That's an attribute I have used many times, without really thinking of its complete application. The most important is as a machine-extractable semantic information tool describing the purpose of an element. It's main application in that regard is for assistive devices (screen readers, magnifying "glasses") to provide information about a page element through to a user who may be sight challenged.
The "role" attribute is abstract in that it can be also used to define document structure.
As I write my Worx CSS classless library, I am mindful to create role attribute names and values that have dual purposes. To assist reading machines, and to assist in meaningful mark up.
One example is in the text utilities, I have a definition that can be used to indicate capitalized text. It would be used as in <h1 role="capitalize-text">heading</h1>.
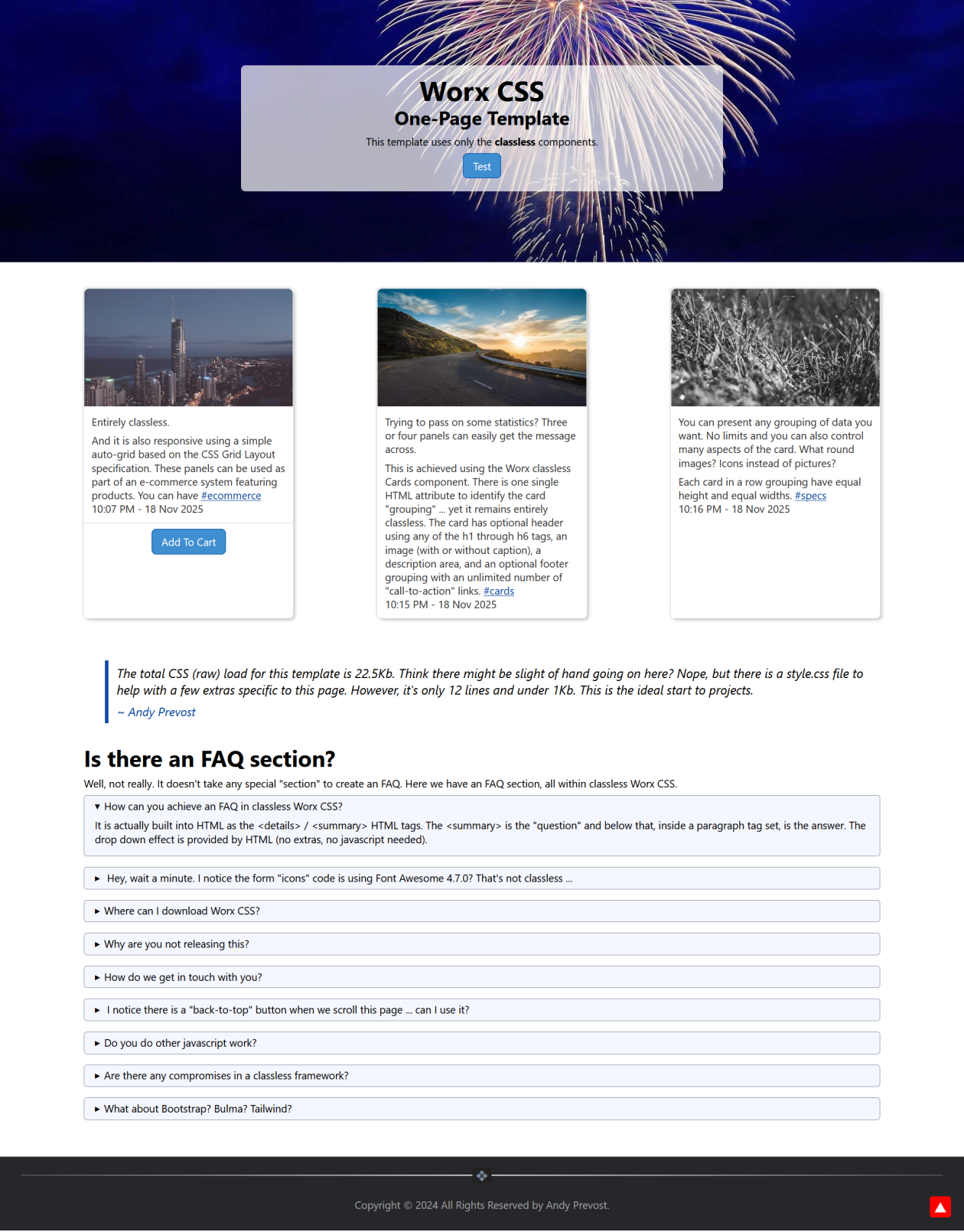
First template created with classless Worx CSS
Click on the image above for a full size version. It's a template being developed to include with Worx CSS when released. And, it's entirely semantic HTML. No classes. The only "extra" in the page is some Javascript for "back-to-top" functionality.